When the power goes out, having a backup generator can be a lifesaver. It keeps your lights on, your appliances running, and ensures that you’re not left in the dark—literally and figuratively. However, to use a generator effectively, you need to know how to wire a generator into your house safely. Improper Wiring can lead to serious risks, including electrical hazards, fire, and damage to your home’s electrical system.
Understanding the Basics of Home Generator Wiring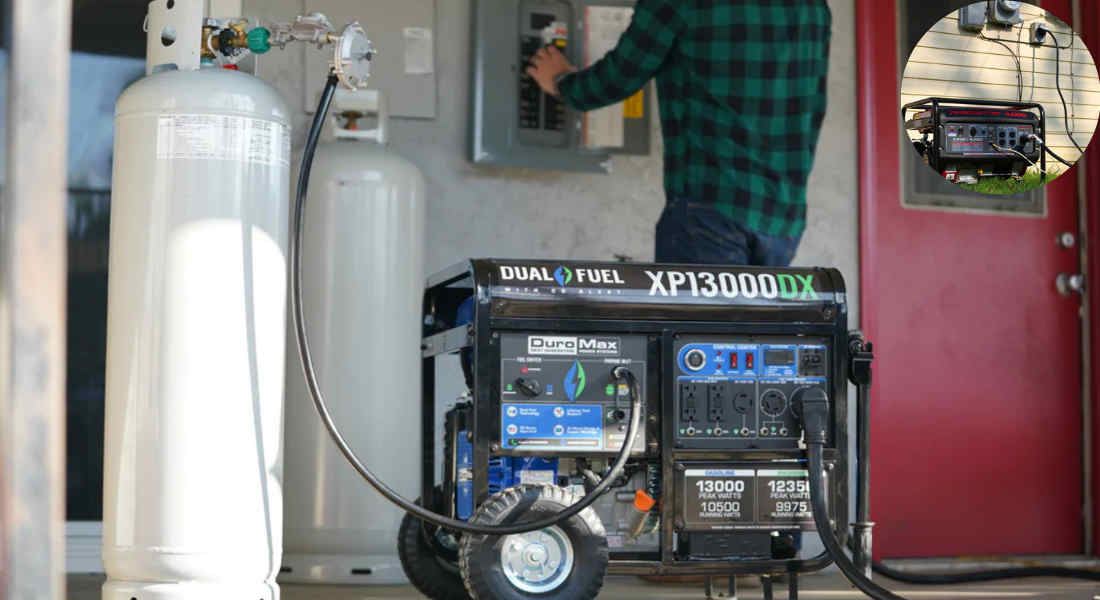
Before you dive into wiring your generator, it’s important to understand the fundamentals of how it works and the components involved. Let’s break it down:
What Does Wiring a Generator to Your Home Mean?
Wiring a generator to your home allows you to connect it to your electrical system so it can supply power during an outage. Instead of plugging in appliances one by one using extension cords, Wiring integrates the generator with your home’s circuit breaker panel, providing power to multiple circuits simultaneously.
Types of Generators Commonly Used for Home Backup Power
There are two primary types of generators:
- Portable Generators: These are smaller, movable units that can power essential appliances during a short-term outage.
- Standby Generators: Permanently installed, these automatically start during a power outage and can power your entire home.
Key Components Involved in Wiring
When wiring a generator to your home, you’ll encounter several critical components:
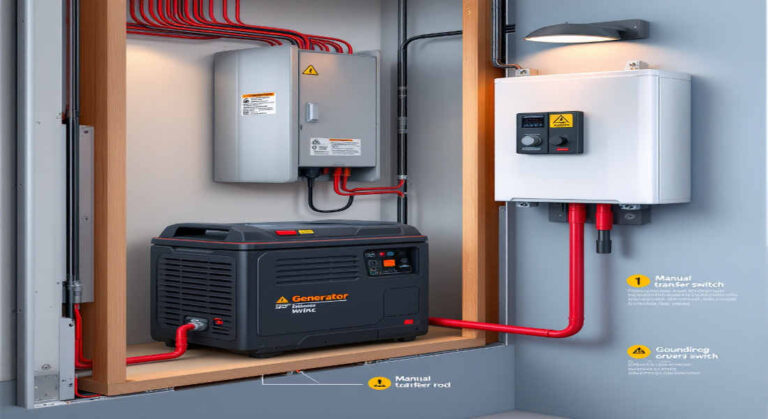
- Transfer Switch: A device that safely switches your home’s power source between the generator and the utility grid.
- Breaker Panel: The main electrical panel in your home, where circuits are connected and managed.
- Power Inlet Box: An outdoor connection point for your generator.
- Generator Cords: Heavy-duty cables designed to handle the electrical load between the generator and your home.
Why Safety Is Paramount When Wiring a Generator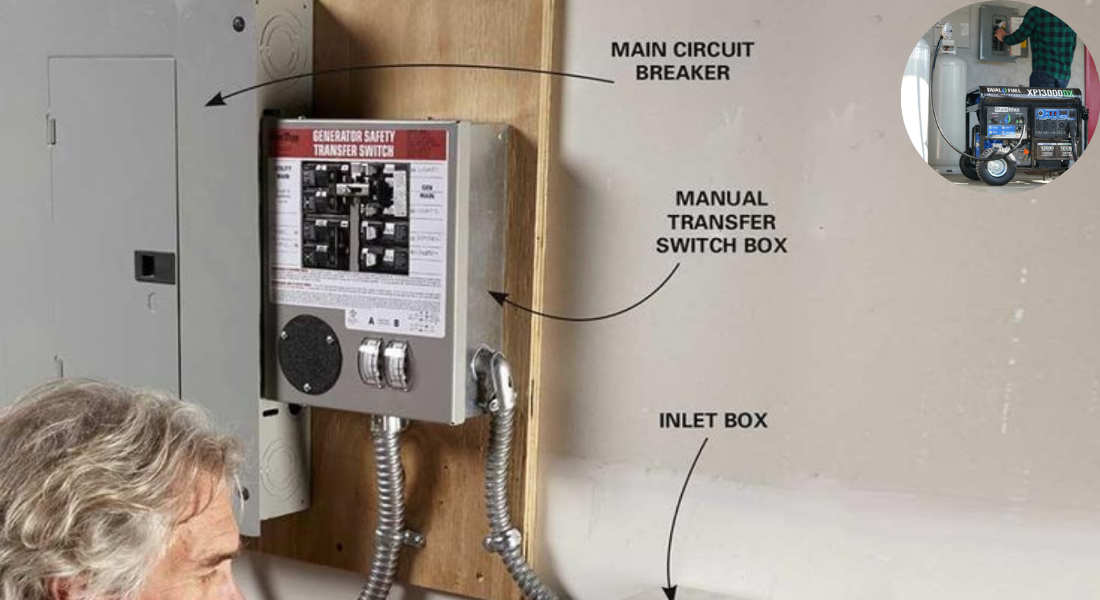
Safety should always be your top priority when dealing with electricity. Wiring a generator improperly can lead to dangerous outcomes.
You may also read (do you pay tax when selling your house).
Risks of Improper Wiring
- Backfeeding: This occurs when electricity flows back into the utility lines, potentially endangering utility workers who are repairing the grid.
- Electrical Shock: Handling live wires without proper precautions can cause severe injuries or even death.
- Fire Hazards: Faulty Wiring or overloaded circuits can result in electrical fires.
Preventing Backfeed and Protecting Utility Workers
A properly installed transfer switch is essential to prevent backfeeding. This switch isolates your home’s electrical system from the utility grid, ensuring that electricity flows in the correct direction.
Legal and Code Compliance
In most areas, wiring a generator to your home must comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC). Some states or municipalities may also require permits or inspections. Adhering to these regulations ensures the safety of your setup and may prevent fines or legal issues.
Essential Equipment for Wiring a Generator to Your Home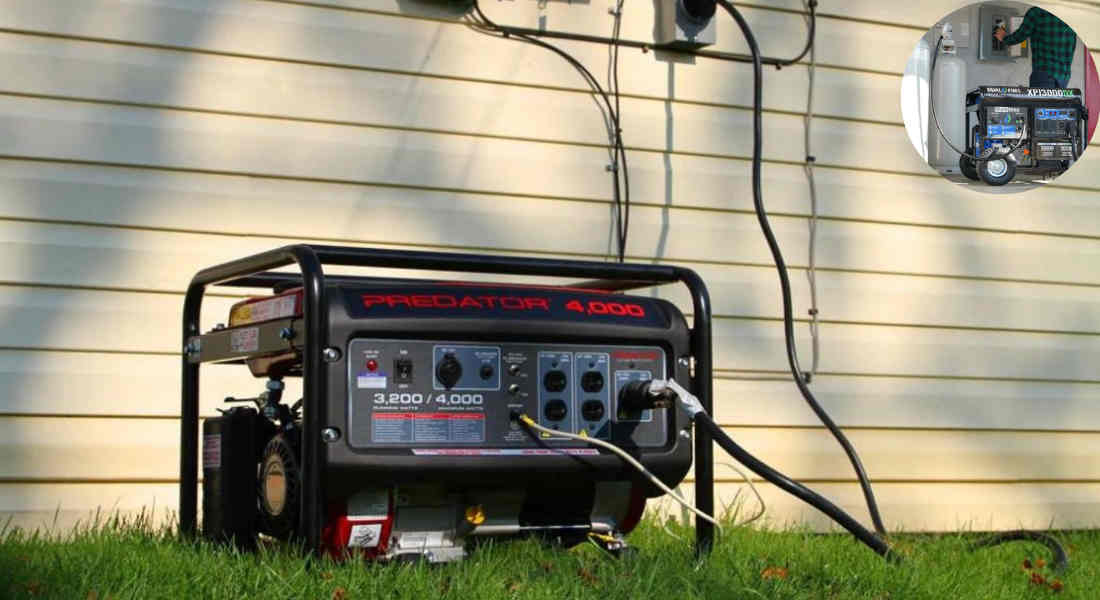
The right equipment is essential for a safe and efficient setup. Here’s what you’ll need:
Transfer Switch: The Safest Option
A transfer switch is a device installed near your breaker panel that lets you switch your power source between the generator and the grid. It prevents backfeeding and allows you to control which circuits are powered during an outage.
Benefits of a Transfer Switch:
- Ensures safety by isolating circuits.
- Simplifies the process of switching power sources.
- Complies with electrical code requirements.
Power Inlet Box
The power inlet box is an outdoor connection point for your generator. It allows you to plug in your generator without running cords through windows or doors.
Advantages:
- Keeps your home secure by avoiding open doors or windows.
- Protects connections from weather and moisture.
Generator Cords and Extension Cords
Use heavy-duty generator cords with the correct gauge to handle the power output of your generator. Avoid using regular extension cords, as they may not be rated for high electrical loads.
Circuit Breaker Interlock Kit
If a transfer switch isn’t an option, a circuit breaker interlock kit can be used as an alternative. While not as convenient, it still provides a safe way to connect a generator to your breaker panel.
You may also read (how can i fix a hot room in my house).
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Wire in a Generator to Your House Safely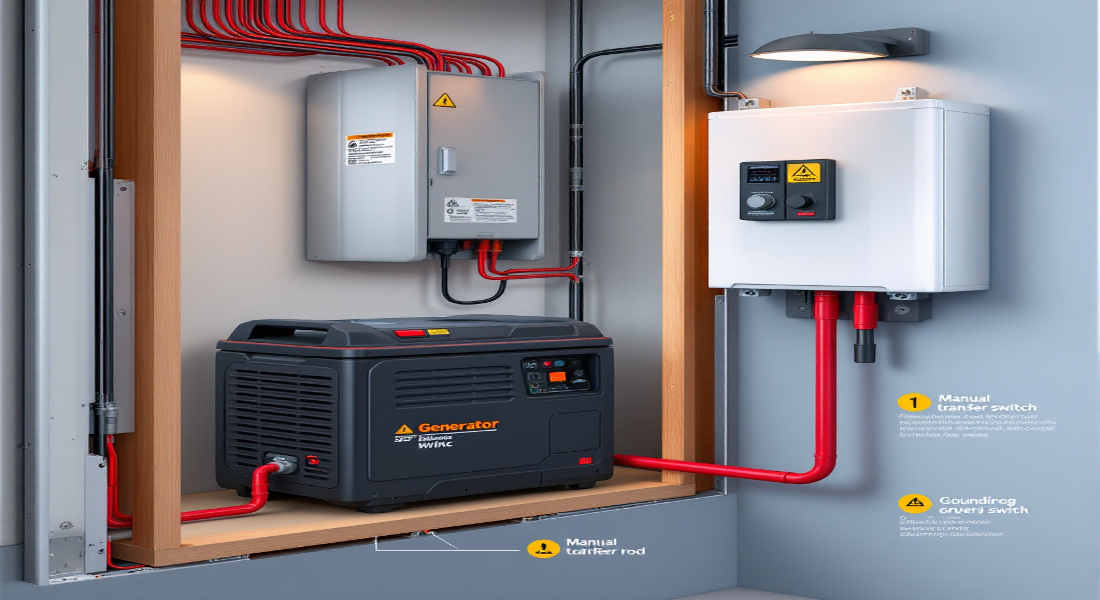
Now that you understand the basics and have the right equipment, let’s go through the process step by step:
Position the Generator Safely
- Place the generator outdoors, at least 15 feet away from your home.
- Ensure the exhaust faces away from windows, doors, or vents to avoid carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Set the generator on a flat, stable surface to prevent tipping.
Turn Off the Main Power
Before connecting your generator, turn off the main power to your home at the breaker panel. This prevents backfeed and protects utility workers.
Install a Transfer Switch or Power Inlet Box
- Transfer Switch: Connect the switch to your breaker panel, wiring it to the circuits you want to power with the generator.
- Power Inlet Box: Install this near your breaker panel and connect it to the transfer switch.
Connect the Generator to the Transfer Switch or Breaker Panel
- Plug one end of the generator cord into the generator and the other into the power inlet box or transfer switch.
- Switch the circuits you want to power to the generator position.
Testing the Setup
- Use a multimeter to check the voltage and ensure connections are correct.
- Gradually activate circuits one by one to avoid overloading the generator.
Alternative Methods and Their Risks
If a transfer switch isn’t an option, there are other methods—but they come with risks:
Using Extension Cords
- Pros: Simple and inexpensive.
- Cons: Limited to powering individual appliances and can be a tripping hazard.
Interlock Kits
- Safer than extension cords but still requires careful installation and use.
Maintenance and Safety Tips for Generator Wiring
- Inspect Wiring Regularly: Check for frayed cords or loose connections.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Each generator has specific maintenance requirements.
- Carbon Monoxide Safety: Always run generators outdoors with proper ventilation.
Legal and Code Compliance Considerations
- Verify compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC).
- Hire a licensed electrician if you’re unsure about any part of the process.
- Obtain necessary permits and schedule inspections when required.
You may also read (home temperature when away in winter).

