Are you a homeowner or a DIY enthusiast looking to tackle some plumbing projects? If so, understanding household plumbing pipe sizes is crucial for a successful outcome. Choosing the correct pipe size can make a world of difference in your home’s water pressure, flow rate, and overall plumbing system efficiency.
Basics of Household Plumbing Pipes
What Are Household Plumbing Pipes?
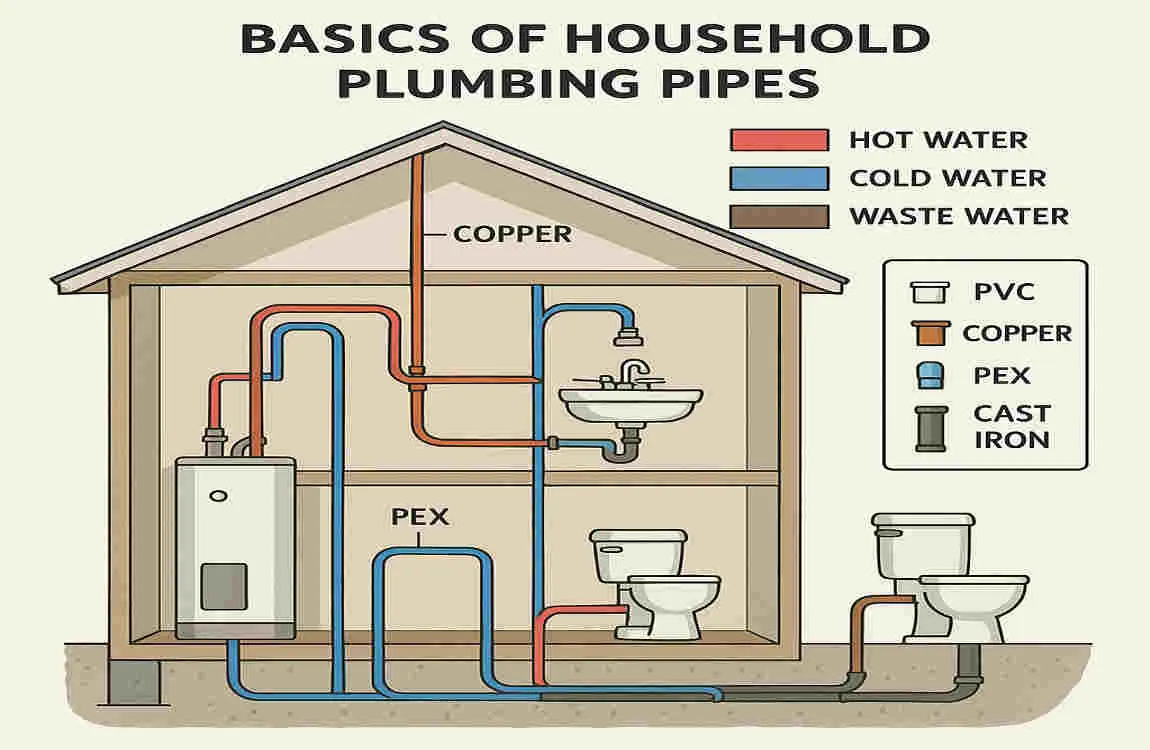
Household plumbing pipes are the unsung heroes of our homes, responsible for delivering clean water and removing waste. These pipes play a vital role in ensuring our comfort and hygiene. They come in various materials, such as copper, PVC, PEX, and galvanized steel, each with its own set of characteristics and applications.
Understanding Pipe Dimensions: Diameter and Length
When it comes to pipe dimensions, it’s essential to understand the difference between nominal and actual diameter. The nominal diameter is the standard size used to identify the pipe, while the actual diameter may vary slightly. The diameter of a pipe directly affects the water flow and pressure within your home’s plumbing system.
Additionally, pipe length is another factor to consider during installation. Pipes come in various lengths, and proper planning is necessary to ensure efficient and cost-effective installation.
Types of Pipes in a Household Plumbing System
In a household plumbing system, there are two main types of pipes: supply pipes and drain pipes. Supply pipes are responsible for delivering fresh water to your fixtures, while drain pipes carry away waste and wastewater.
The materials used for these pipes differ, with supply pipes often made of copper, PEX, or PVC, and drain pipes typically made of PVC or ABS. The sizing of these pipes also varies, as we’ll explore in the next section.
Common Household Plumbing Pipe Sizes
Standard Pipe Sizes for Water Supply Lines
You may also read (how to safely turn off your home gas line).
When it comes to water supply lines, there are a few standard pipe sizes that you’ll commonly encounter in households:
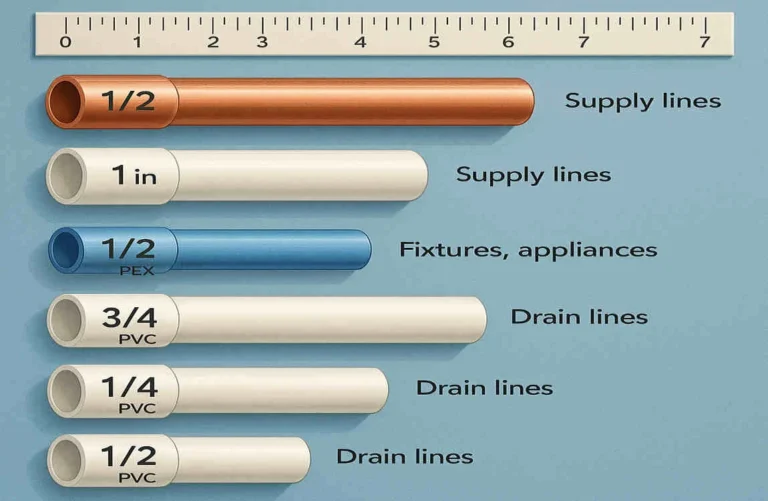
- ½ inch: These pipes are typically used for individual fixtures, such as sinks and showers.
- ¾ inch: These pipes are often used as main distribution lines, supplying water to multiple fixtures.
- 1 inch: Larger main supply lines may use 1-inch pipes to ensure adequate water flow throughout the home.
Here’s a handy table summarising these standard supply pipe sizes and their typical uses:
Pipe SizeTypical Use
½ inch Individual fixtures (sinks, showers)
¾ inch Main distribution lines
1 inch Larger main supply lines
Standard Pipe Sizes for Drainage and Waste Lines
Drainage and waste lines require larger pipe sizes to handle the volume of water and waste they carry. Here are some standard sizes:
- 1 ½ inch to 2 inch: These pipes are typically used for sinks and showers.
- 3 inches or more: Toilets and main waste lines often require pipes of 3 inches or larger to handle the increased volume.
The reason drainage pipes are larger than supply pipes is to prevent clogs and ensure proper flow. A larger diameter allows for more efficient removal of waste and wastewater from your home.
Pipe Size Recommendations for Popular Household Fixtures
Different household fixtures have specific pipe size recommendations for both supply and drain lines. Here’s a quick overview:
- Kitchen sink:
- Supply: ½ inch
- Drain: 1 ½ inch
- Bathroom sink:
- Supply: ½ inch
- Drain: 1 ½ inch
- Bathtub/shower:
- Supply: ½ inch
- Drain: 1 ½ inch to 2 inch
- Toilet:
- Supply: ½ inch
- Drain: 3 inches or more
- Washing machine:
- Supply: ½ inch
- Drain: 1 ½ inch to 2 inch
For a quick reference, here’s a chart summarising these pipe size recommendations:
Fixture Supply Pipe Size Drain Pipe Size
Kitchen sink ½ inch 1 ½ inch
Bathroom sink ½ inch 1 ½ inch
Bathtub/shower ½ inch 1 ½ inch to 2 inch
Toilet ½ inch , 3 inch or more
Washing machine ½ inch 1 ½ inch to 2 inch
How to Choose the Right Pipe Size for Your Home
Factors Influencing Pipe Size Selection
Selecting the correct pipe size for your home involves considering several factors:
- Water pressure: The water pressure in your home and the municipality’s supply can impact the required pipe size.
- Number and types of fixtures: The more fixtures you have, the larger the pipe size may need to be to ensure adequate flow.
- Distance from the main supply: The distance between your main water supply and individual fixtures can affect the necessary pipe size.
- Local plumbing codes and regulations: Always check with your local authorities to ensure compliance with plumbing codes and regulations.
Understanding Water Supply Fixture Units (WSFU)
You may also read (top materials needed to build a house a complete 2025 guide).
Water Supply Fixture Units (WSFU) are a standardised way of measuring the water demand of various fixtures. Understanding WSFU is crucial for determining the appropriate pipe size for your home.
To calculate your home’s total fixture units, you’ll need to add up the WSFU values for each fixture. These values can be found in plumbing codes or manufacturer specifications. Once you have the total, you can use it to determine the required pipe size based on standard sizing charts.
Using Pipe Sizing Charts and Tables
Pipe sizing charts and tables are invaluable tools for selecting the correct pipe size for your home. These charts provide a quick and easy way to determine the appropriate size based on factors like water pressure, flow rate, and fixture units.
To use these charts, simply locate the row that corresponds to your water pressure and the column that matches your total fixture units. The intersection of these two values will give you the recommended pipe size.
Let’s walk through an example sizing scenario for a typical home:
Imagine you have a two-story home with the following fixtures:
- 2 kitchen sinks (2 WSFU each)
- 2 bathroom sinks (1 WSFU each)
- 2 toilets (3 WSFU each)
- 2 showers (2 WSFU each)
- 1 washing machine (1.5 WSFU)
Your total fixture units would be: (2 x 2) + (2 x 1) + (2 x 3) + (2 x 2) + 1.5 = 18.5 WSFU
If your water pressure is 40 psi, according to a standard sizing chart, you would need a ¾ inch pipe for the main supply line to accommodate your total fixture units.
Tips for Pipe Sizing on Multi-story Homes
When it comes to multi-story homes, pipe sizing can be a bit more complex. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Consider the vertical distance: Water needs to be delivered to upper floors, which can impact the required pipe size. As a general rule, you may need to increase the pipe size for each floor to maintain adequate pressure and flow.
- Balance the system: Ensure that the pipe sizes are balanced throughout the system to prevent pressure imbalances between floors.
- Consult a professional: If you’re unsure about sizing pipes in a multi-story home, it’s always best to consult a licensed plumber who can provide expert guidance.
Impact of Incorrect Pipe Sizing
Problems Caused by Undersized Pipes
Using undersized pipes in your home’s plumbing system can lead to a host of issues:
- Low water pressure and flow rate: Undersized pipes restrict the flow of water, resulting in reduced pressure and flow at your fixtures.
- Increased wear and noise: When water flows through undersized pipes, it can cause increased wear on the pipes and create more noise as it struggles to move through the system.
- Potential damage and leaks: The increased pressure caused by undersized pipes can lead to leaks and even pipe bursts, resulting in costly damage to your home.
Issues with Oversized Pipes
While undersized pipes can cause problems, oversized pipes can also lead to issues:
- Increased material and installation costs: Using larger pipes than necessary can increase the cost of materials and installation.
- Possible water stagnation in unused pipes: Oversized pipes can lead to water stagnation in unused sections, which can result in the growth of bacteria and other contaminants.
- Unnecessary strain on water heaters and pumps: Larger pipes require more water to fill, which can put unnecessary strain on your water heater and pumps, leading to increased energy consumption and potential equipment failure.
Importance of Professional Advice and Permits
When it comes to plumbing projects, it’s always wise to seek professional advice and obtain the necessary permits:
- Consult a licensed plumber: If you’re unsure about pipe sizing or any other aspect of your plumbing project, a licensed plumber can provide expert guidance and ensure that your system is designed and installed correctly.
- Follow local codes: Always check with your local authorities to ensure that your plumbing project complies with all relevant codes and regulations. Obtaining the necessary permits can help you avoid costly fines and ensure that your work meets safety standards.
Modern Trends and Innovations in Plumbing Pipes

New Materials Affecting Pipe Size Choices
The world of plumbing pipes is constantly evolving, with new materials and technologies influencing pipe size choices:
- Flexible PEX pipes: PEX (cross-linked polyethene) pipes have gained popularity in recent years due to their flexibility, ease of installation, and corrosion resistance. These pipes can be bent and curved, reducing the need for fittings and potentially affecting the required pipe size.
- Changes in sizing due to new materials: As new materials like PEX become more widely used, sizing charts and recommendations may change to accommodate their unique properties. It’s essential to stay up-to-date with the latest information when selecting pipe sizes for your home.
Smart Plumbing Solutions and Sizing Integration
Technology is also making its way into the world of plumbing, with innovative solutions that can influence pipe sizing:
- Smart water meters and leak detection systems can help you monitor your home’s water usage and detect potential issues before they become significant problems. These technologies may impact pipe sizing by providing more accurate data on your home’s water demands.
- Integrated home automation: As home automation systems become more prevalent, they may be integrated with plumbing systems to optimise water usage and efficiency. This integration could lead to changes in pipe sizing recommendations to accommodate the increased control and monitoring capabilities.
You may also read (easy guide to cutting house copper pipes).